Introduction
Fertilizers play a pivotal role in modern agriculture, significantly affecting both soil health and crop yields. As global food demands rise, the use of fertilizers has become essential for enhancing agricultural productivity. However, the relationship between fertilizers, soil health, and environmental sustainability is complex. While fertilizers can provide essential nutrients that promote plant growth, their overuse or misuse can lead to detrimental effects on soil quality and the surrounding ecosystem. Understanding this balance is crucial for farmers aiming to optimize crop production while maintaining soil health. This article will delve into the impact of fertilizers on soil health and crop yields, examining both the benefits and potential drawbacks of their use in agriculture.
The Role of Fertilizers in Agriculture
1. Nutrient Supply
Fertilizers are primarily used to supply essential nutrients that plants need for growth. The three primary nutrients provided by most fertilizers are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), often referred to as N-P-K.
- Nitrogen: Essential for leaf and stem growth, nitrogen promotes lush vegetative development.
- Phosphorus: Important for root development, flowering, and fruiting.
- Potassium: Aids in overall plant health, enhancing disease resistance and water regulation.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), proper fertilizer application can increase crop yields by 20-50%, helping farmers meet growing food demands.
2. Enhancing Crop Yields
The application of fertilizers has been instrumental in boosting agricultural productivity. Fertilizers provide a readily available source of nutrients that can lead to significant increases in crop yields.
- Research Findings: A study published in “Agricultural Systems” found that fertilizer application increased maize yields by an average of 30% across various regions.
3. Soil Health Considerations
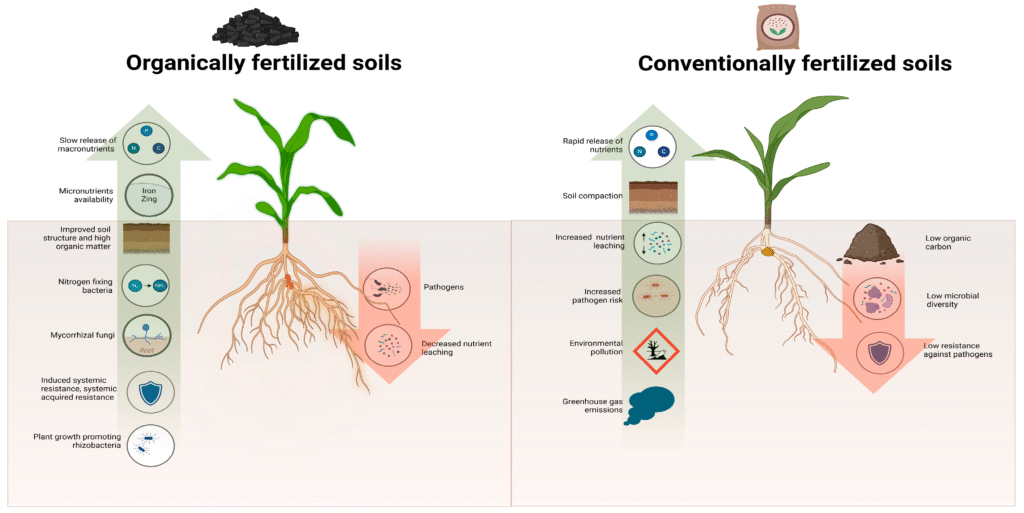
While fertilizers can enhance crop production, their impact on soil health cannot be overlooked. The following points highlight both positive and negative effects:
Positive Effects:
- Nutrient Enrichment: Fertilizers can replenish nutrient-depleted soils, improving fertility.
- Microbial Activity: Some organic fertilizers enhance microbial populations that contribute to nutrient cycling.
Negative Effects:
- Soil Acidification: Overuse of nitrogen-based fertilizers can lead to soil acidification, which negatively impacts nutrient availability.
- Nutrient Imbalance: Excessive application may result in nutrient imbalances, leading to deficiencies in other essential elements.
The Environmental Impact of Fertilizer Use
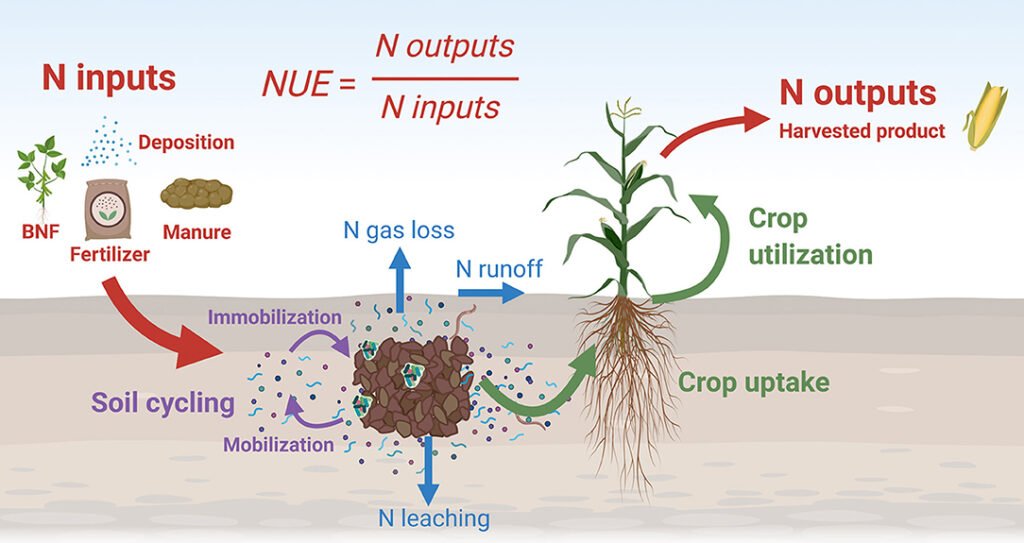
1. Nutrient Runoff
One of the significant environmental concerns associated with fertilizer use is nutrient runoff. When excess fertilizers are applied, nutrients can leach into waterways during rainfall or irrigation events.
- Consequences: This runoff contributes to water pollution, causing issues such as algal blooms that deplete oxygen levels in aquatic ecosystems.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), nutrient pollution is a leading cause of water quality degradation in many regions.
2. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The production and application of synthetic fertilizers contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Nitrous Oxide Emissions: Nitrogen-based fertilizers release nitrous oxide (N2O), a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
Research from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) indicates that agricultural practices account for approximately 10-12% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with fertilizer use being a significant factor.
Best Practices for Fertilizer Use

To maximize the benefits of fertilizers while minimizing their negative impacts on soil health and the environment, farmers can adopt several best practices:
1. Soil Testing
Conducting regular soil tests helps determine nutrient levels and pH balance, allowing for tailored fertilizer applications based on actual needs.
- Benefits: Soil testing can lead to more efficient fertilizer use, reducing waste and costs while improving crop yields.
2. Integrated Nutrient Management
Combining organic and chemical fertilizers can optimize nutrient availability while enhancing soil health.
- Approach: Organic amendments such as compost or manure can improve soil structure and microbial activity while chemical fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability.
3. Precision Application Techniques
Utilizing precision agriculture techniques allows farmers to apply fertilizers based on specific field conditions rather than blanket applications.
- Technologies: GPS-guided equipment and soil moisture sensors enable targeted applications that reduce waste and environmental impact.
4. Crop Rotation
Implementing crop rotation helps maintain nutrient balance in the soil by alternating crops with different nutrient requirements.
- Benefits: This practice reduces pest populations and enhances overall soil fertility.
Conclusion
The impact of fertilizers on soil health and crop yields is multifaceted. While they are essential for enhancing agricultural productivity, their misuse can lead to significant environmental challenges. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of different types of fertilizers, farmers can make informed decisions that optimize crop yields while promoting sustainable practices. As we strive for food security amid increasing pressures from climate change, adopting responsible fertilizer management becomes crucial for building resilient agricultural systems that protect both our soils and our environment.
Evaluate your fertilization practices today—consider implementing best practices that enhance productivity while safeguarding soil health!
Q&A Section
Q: How do fertilizers affect soil health?
A: Fertilizers can enhance soil fertility by replenishing nutrients; however, overuse can lead to acidification, nutrient imbalances, and degradation of soil structure.
Q: What are some best practices for using fertilizers?
A: Best practices include conducting soil tests, utilizing integrated nutrient management strategies, applying precision techniques, and implementing crop rotation.
Q: Can organic fertilizers improve soil health?
A: Yes! Organic fertilizers enhance microbial activity and improve soil structure over time while providing essential nutrients for crops.
Resources
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- American Society of Agronomy
- Sustainable Agriculture Research & Education (SARE)
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)







